The Republic of Ghana, is a unitary presidential constitutional democracy, located along the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean, in the subregion of West Africa. Spanning a land mass of 238,535 km², Ghana is bordered by the Ivory Coast in the west, Burkina Faso in the north, Togo in the east and the Gulf of Guinea and Atlantic Ocean in the south. Ghana means "Warrior King" in the Soninke language.
Ghana

Location
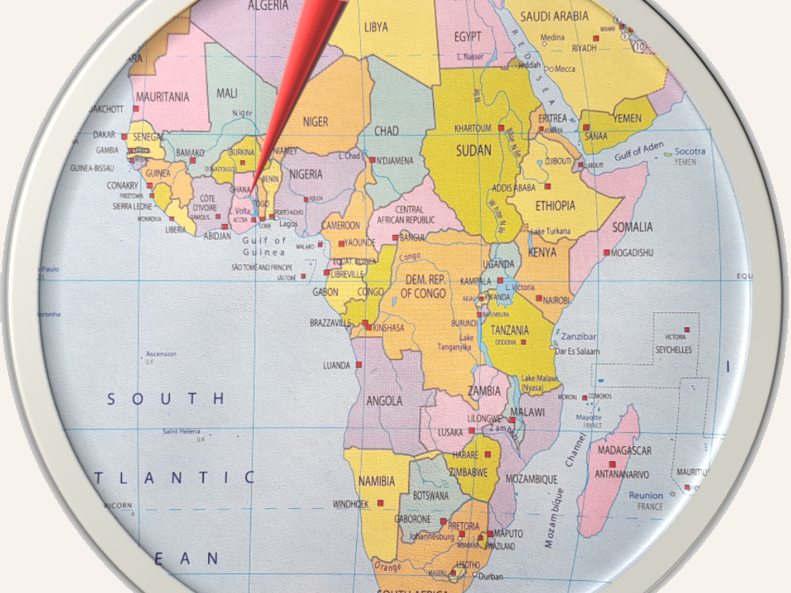

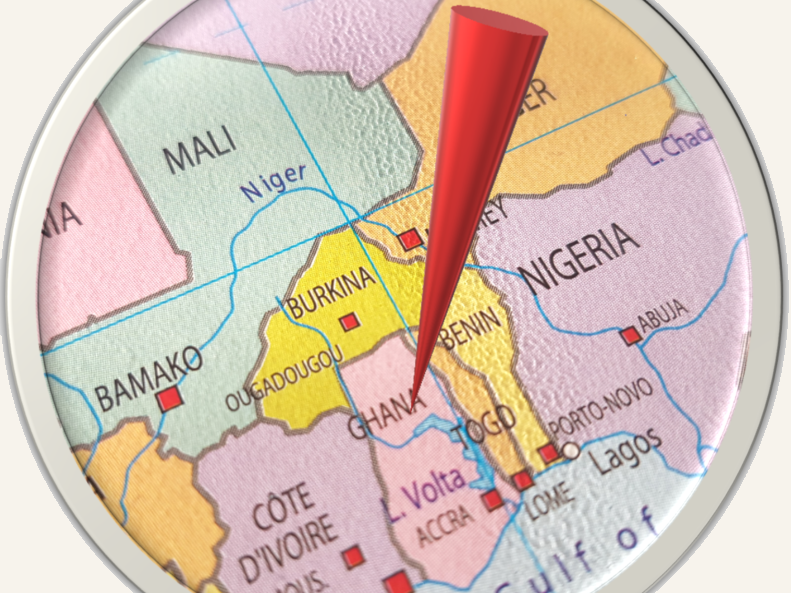
Geographically Ghana is estimated to be the closest country to the center of the earth. It is also located in closer proximity, north of the equator, thus Ghana mostly has tropical warm climate. The latitudinal extent of Ghana is 4° to 12°N latitudes and 4°W to 2°E longitudes. The prime meridian passes through the town of Tema in Ghana. Accra is the capital city of Ghana.
Vegetation and Clime
Grasslands mixed with south coastal shrublands and forests dominate Ghana, with forest extending northward from the south-west coast of Ghana on the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean 320 kilometres (200 miles) and eastward for a maximum of about 270 kilometres (170 miles) with the Kingdom of Ashanti or the southern part of Ghana being a primary location for mining of industrial minerals and timber.
Religion



Ghana is a largely Christian country, although a sizable Muslim minority exists. Traditional (indigenous) beliefs are also practiced.
History

The territory of present-day Ghana has been inhabited for a millennium, with the first permanent state dating back to the 11th century. Numerous kingdoms and empires emerged over the centuries, of which the most powerful was the Kingdom of Ashanti. Beginning in the 15th century, numerous European powers contested the area for trading rights, with the British ultimately establishing control of the coast by the late 19th century. Following over a century of native resistance, Ghana's current borders were established by the 1900s as the British Gold Coast. On 6 March 1957, it became the first sub-Saharan African nation to become independent of European colonisation.

A multicultural nation, Ghana has a population of approximately 27 million, spanning a variety of ethnic, linguistic and religious groups. Five percent of the population practices traditional faiths, 71.2% adhere to Christianity and 17.6% are Muslim. Its diverse geography and ecology ranges from coastal savannahs to tropical jungles. Ghana is a democratic country led by a president who is both head of state and head of the government. Ghana's economy is one of the strongest and most diversified in Africa, following a quarter century of relative stability and good governance. Ghana's growing economic prosperity and democratic political system have made it a regional power in West Africa. It is a member of the Non-Aligned Movement, the African Union, the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS), Group of 24 (G24) and the Commonwealth of Nations.
Politics

Ghana is a unitary presidential constitutional democracy with a parliamentary multi-party system and former alternating military occupation. Following alternating military and civilian governments in January 1993, the Ghana military government gave way to the Fourth Republic of Ghana after presidential elections and parliamentary elections in late 1992. The 1992 constitution of Ghana divides powers among a Commander-in-Chief of the Ghana Armed Forces (President of Ghana), parliament (Parliament of Ghana), cabinet (Ministers of the Ghanaian Government), council of state (Ghanaian Council of State), and an independent judiciary (Judiciary of Ghana). The Government of Ghana is elected by universal suffrage after every four years.
The Electoral Commission of Ghana announced that former Vice President of Ghana John Dramani Mahama had won the Ghana presidential election, 2012 on 7 December 2012 and John Dramani Mahama was sworn in, amidst announcement of electoral fraud, as the reigning President of Ghana on 7 January 2013 to serve a four-year term that expired on Saturday, 7 January 2017.
The 2012 Fragile States Index indicated that Ghana is ranked the 67th least fragile state in the world and the 5th least fragile state in Africa after Mauritius, 2nd Seychelles, 3rd Botswana, and 4th South Africa. Ghana ranked 112th out of 177 countries on the index. Ghana ranked as the 64th least corrupt and politically corrupt country in the world out of all 174 countries ranked and Ghana ranked as the 5th least corrupt and politically corrupt country in Africa out of 53 countries in the 2012 Transparency International Corruption Perception Index. Ghana was ranked 7th in Africa out of 53 countries in the 2012 Ibrahim Index of African Governance. The Ibrahim Index is a comprehensive measure of African government, based on a number of different variables which reflect the success with which governments deliver essential political goods to its citizens.
Economy

Ghana is an average natural resource enriched country possessing industrial minerals, hydrocarbons and precious metals. It is an emerging designated digital economy with mixed economy hybridisation and an emerging market with 8.7% GDP growth in 2012. It has an economic plan target known as the "Ghana Vision 2020". This plan envisions Ghana as the first African country to become a developed country between 2020 and 2029 and a newly industrialised country between 2030 and 2039. This excludes fellow Group of 24 member and Sub-Saharan African country South Africa, which is a newly industrialised country. Ghana's economy also has ties to the Chinese yuan renminbi along with Ghana's vast gold reserves. In 2013, the Bank of Ghana began circulating the renminbi throughout Ghanaian state-owned banks and to the Ghana public as hard currency along with the national Ghana cedi for second national trade currency.
The state-owned Volta River Authority and Ghana National Petroleum Corporation are the two major electricity producers. The Akosombo Dam, built on the Volta River in 1965, along with Bui Dam, Kpong Dam, and several other hydroelectric dams provide hydropower. In addition, the Government of Ghana has sought to build the second nuclear power plant in Africa.
The Ghana Stock Exchange is the 5th largest on continental Africa and 3rd largest in sub-saharan Africa with a market capitalisation of GH¢ 57.2 billion or CN¥ 180.4 billion in 2012 with the South Africa JSE Limited as first.[100] The Ghana Stock Exchange (GSE) was the 2nd best performing stock exchange in sub-saharan Africa in 2013.
Ghana also produces high-quality cocoa, is the 2nd largest producer of cocoa globally, and is projected to become the world's largest producer of cocoa in 2015.
Ghana is classified as a middle income country. Services account for 50% of GDP, followed by manufacturing (24.1%), extractive industries (5%), and taxes (20.9%).
Agriculture

Agriculture in Ghana consists of a variety of agricultural products and is an established economic sector, and provides employment on a formal and informal basis. Ghana produces a variety of crops in various climatic zones which range from dry savanna to wet forest and which run in eastwest bands across Ghana. Agricultural crops, including yams, grains, cocoa, oil palms, kola nuts, and timber, form the base of agriculture in Ghana's economy In the year of 2013, agriculture employed 53.6% of the total labor force in Ghana.
State budget

2016 budget: GHc50 billion.
